Crypto
Cryptocurrencies: A glimpse into the future of money
Cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum have shot into the consciousness of investors and the tech-savvy. Will these replace money as we know it?

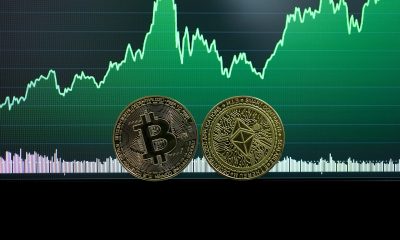
There’s a lot of buzz about the fact that Ethereum, one of the more popular cryptocurrencies (the other one is Bitcoin) went down by 20 percent in value on Monday, June 26th. CNBC reported that the reason for the drop has yet to be determined, but one factor could be the rumor that Ethereum founder Vitalik Buterin had died. Buterin tweeted a photo of himself to dispel the false news.
Still, it’s unlikely that such a drop would turn people away from Ethereum or Bitcoin, or other cryptocurrencies available today. To know why it’s better to get a deeper understanding of what cryptocurrencies are and what they mean for the world in the future.
Essentially, cryptocurrencies represent the future of money. Again to understand why that is, one has to delve deeper. What is money, anyway? Of itself, money has no value. It’s just paper or a piece of metal, or in previous ages, pieces of stone or wood, or seashells. What gives money value is civilization’s collective agreement to assign a value to it, to make it a medium for transactions and the exchange of goods and services. Or as the TEDTalk by Neha Narula puts it, money is fiction that we all go along with.
Narula’s talk is one of the best explanations for the concept of money and how cryptocurrencies will change it. One example is how money is digitally transferred today. When a credit card is used, or when an online money transfer or purchase is made, no actual paper bills or coins are exchanged. Instead, the money is represented digitally by ones and zeroes. And yet, there’s value to these digital representations because huge financial institutions like credit card companies and banks back or underwrite that value. They guarantee that these monetary transactions are valid.

Bitcoin and Ethereum are the best-known cryptocurrencies today. (Source)
Cryptocurrencies are different in one fundamental way. They are money that can be spent, transferred, and received without the intermediary or underwriting role played by banks, etc. In short, they allow person-to-person money transactions to happen directly while taking the banks and other financial institutions out of the loop. They represent the true democratization of money.
Furthermore, they also make transactions cheaper: there are no more intermediaries involved charging, say, 10 to 20 percent for an overseas money transfer. Cryptocurrency transactions are also faster. A regular bank transfer can take days or weeks. Cryptocurrencies are exchanged in minutes or seconds. Another benefit is that cryptocurrencies are presently very hard to hack. Not so for banks and other financial companies which have lost millions upon millions of dollars to hackers.
The technology behind cryptocurrencies
What makes all these possible for cryptocurrencies? It all has to do with the technology that creates, exchanges and secures them. That technology is called a “blockchain.” The simple explanation for it is this: for every cryptocurrency transaction, a record is made (as in a ledger), time stamped, and stored in millions of computers around the world simultaneously. All these records are strung together, chronologically, in real time, in blocks of information. These blocks are arranged in chains that are updated every ten minutes.
Each new block is added to the previous blocks in the chain. This represents a record of present and previous transactions that are verifiable through data kept in millions of computers around the world. The data is also encrypted using the latest technology and the most advanced and powerful computers.
This is what makes cryptocurrency transactions “unhackable” at the moment. To modify, falsify, or fake a cryptocurrency transaction, one would have to break the encryption and change the data in all the blocks in all the chains in all the millions of computers in the worldwide network. Not easy to do.
Now, where does all this currency, this money, come from? From computer codes and programs. To create units of cryptocurrency, say, a Bitcoin, there are people called Bitcoin miners. These miners use computer programs to solve puzzles. Once a puzzle is solved, Bitcoins are generated. This adds to the world’s store of Bitcoins.
Not everyone can do this. For example, using even the most powerful laptop, it can take millions of years to solve a puzzle. Bitcoin miners use the most advanced programs and hardware to solve such puzzles in a short time.
So are we ready for the future of money? As with every new technology, there will be glitches and even dangers as it develops and gains wider use. For example, cryptocurrencies can be used to hide illegal transactions that benefit criminals or terrorists. And yet, it’s where our money is headed, hopefully for the good of everyone.

-

 Crypto2 weeks ago
Crypto2 weeks agoBitcoin Steady Near $68K as ETF Outflows and Institutional Moves Shape Crypto Markets
-

 Business7 days ago
Business7 days agoDow Jones Stalls Near Record Highs as Inflation-Fueled Rally Awaits Next Move
-

 Fintech4 days ago
Fintech4 days agoFirst Regulated Blockchain Stock Trade Launches in the United States
-

 Africa2 weeks ago
Africa2 weeks agoAir Algérie Expands African Partnerships





















You must be logged in to post a comment Login