Impact Investing
Global Warming: In 2024 the World Will Have Passed the Critical Threshold of 1.5 Degrees
2024 was the hottest year on record, surpassing 1.5°C above pre-industrial levels, breaching the Paris Agreement’s critical limit. Driven by greenhouse gas emissions, this milestone intensifies extreme weather, rising seas, and biodiversity loss. Impacts threaten global food, water, and human health. Urgent, coordinated action with renewable energy investment is vital to mitigate climate catastrophe.
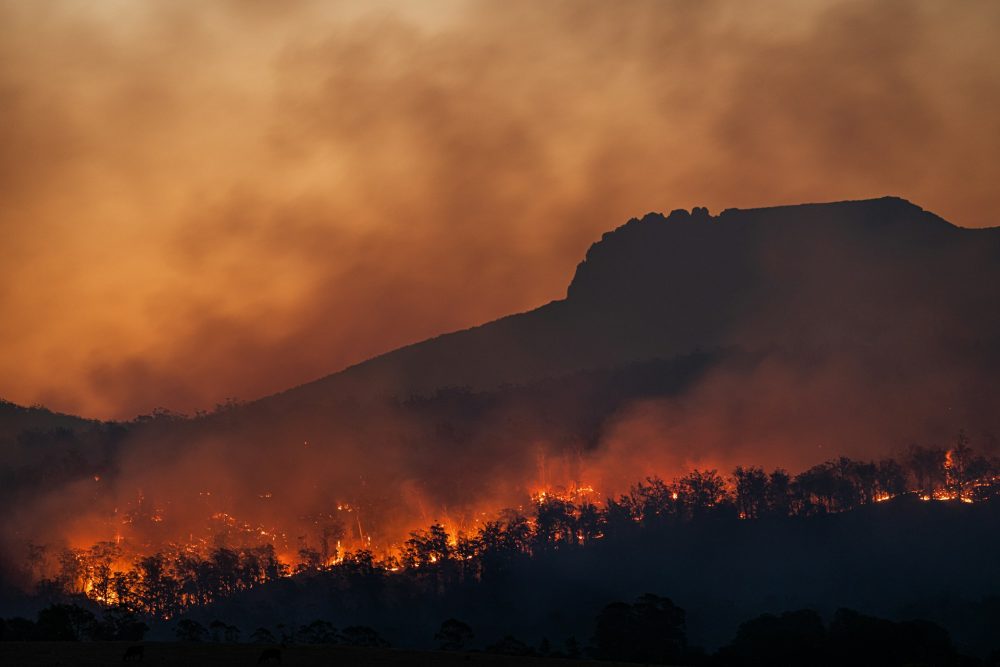

2024 was a year marked by extreme weather events around the world, with record heatwaves, prolonged droughts and an intensification of weather phenomena such as hurricanes and typhoons, all because of the global warming.
But what makes this year truly exceptional is an unequivocal scientific fact: 2024 was the hottest year on record, exceeding the critical threshold of 1.5 degrees Celsius above pre-industrial levels.
A red alert from the planet
Data from the Copernicus Climate Change Service (C3S), the European Union’s climate monitoring service, confirm that the 2024 global average temperature will have exceeded the 1850-1900 average by more than 1.5 degrees Celsius.
This exceeding of the threshold, established as the upper limit to avoid the worst impacts of climate change in the 2015 Paris Agreement, is a wake-up call for humanity. Despite numerous Conferences of the Parties (COPs), including the recent COP29 in Azerbaijan, international efforts to combat climate change have proven insufficient, lacking ambition and concrete political decisions.
Causes of exceeding the 1.5 degrees Celsius threshold
The excessive accumulation of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere, mainly carbon dioxide (CO₂) and methane (CH₄), resulting from human activities such as fossil fuel combustion and deforestation, is the main driver of global warming. This accumulation alters the Earth’s radiative budget, increasing the natural greenhouse effect and causing a significant increase in global mean temperature.
Natural phenomena such as El Niño, although contributing variably to annual temperature fluctuations, are not sufficient to explain the long-term warming trend. Furthermore, the decrease in snow and ice cover, with consequent reduction of the Earth’s albedo, amplifies the warming effect.
The consequences of the global warming for our future
Exceeding the 1.5 degrees Celsius threshold triggers a complex series of chain reactions that profoundly reshape our planet. According to IPCC reports and United Nations projections, further global warming will expose billions of people to extreme heat waves, prolonged droughts and increasingly frequent and intense floods. These extreme events threaten infrastructure, agriculture and ecosystems, jeopardizing the food and water security of millions of people.
At the same time, rising sea levels, caused by melting glaciers and thermal expansion of the oceans, erode coastlines, flood low-lying areas and put coastal communities at risk. The oceans, absorbing a significant portion of atmospheric carbon dioxide, are undergoing a process of acidification that threatens marine biodiversity, compromising the survival of many marine species, from coral reefs to molluscs.
The loss of biodiversity, in turn, destabilizes ecosystems and reduces nature’s ability to provide essential services to humans. The consequences of climate change also affect human health, increasing the incidence of heat-related diseases, allergies and vector-borne diseases. Finally, climate change can trigger conflicts and mass migrations, putting the social and economic stability of many regions of the world at risk.
The chain reaction triggered by exceeding 1.5 degrees Celsius represents an unprecedented challenge for humanity. The economic and social consequences of such an overshoot are set to be profound and far-reaching, putting at risk the stability of entire political and economic systems. A global and coordinated approach is needed to address this crisis, requiring massive investments in renewable energy, energy efficiency and research and development of innovative technologies.
__
(Featured image by Matt Palmer via Unsplash)
DISCLAIMER: This article was written by a third party contributor and does not reflect the opinion of Born2Invest, its management, staff or its associates. Please review our disclaimer for more information.
This article may include forward-looking statements. These forward-looking statements generally are identified by the words “believe,” “project,” “estimate,” “become,” “plan,” “will,” and similar expressions. These forward-looking statements involve known and unknown risks as well as uncertainties, including those discussed in the following cautionary statements and elsewhere in this article and on this site. Although the Company may believe that its expectations are based on reasonable assumptions, the actual results that the Company may achieve may differ materially from any forward-looking statements, which reflect the opinions of the management of the Company only as of the date hereof. Additionally, please make sure to read these important disclosures.
First published in ESG NEWS. A third-party contributor translated and adapted the article from the original. In case of discrepancy, the original will prevail.
Although we made reasonable efforts to provide accurate translations, some parts may be incorrect. Born2Invest assumes no responsibility for errors, omissions or ambiguities in the translations provided on this website. Any person or entity relying on translated content does so at their own risk. Born2Invest is not responsible for losses caused by such reliance on the accuracy or reliability of translated information. If you wish to report an error or inaccuracy in the translation, we encourage you to contact us

-

 Crowdfunding1 week ago
Crowdfunding1 week agoBSG Stahl Riesa Launches Crowdfunding for New Floodlights
-

 Cannabis6 days ago
Cannabis6 days agoSnoop Dogg Searches for the Lost “Orange” Cannabis Strain After Launching Treats to Eat
-

 Crypto2 weeks ago
Crypto2 weeks agoIntesa Sanpaolo Signals Institutional Shift With Major Bitcoin ETF Investments
-

 Cannabis1 day ago
Cannabis1 day agoBrewDog Sale Leaves Thousands of Crowdfunding Investors Empty-Handed