Business
The benefits and challenges of ethanol production in the US
Greenbelt Resources Corp. has developed a system that can sustainably produce bioethanol, which can help lower oil exports in the U.S.
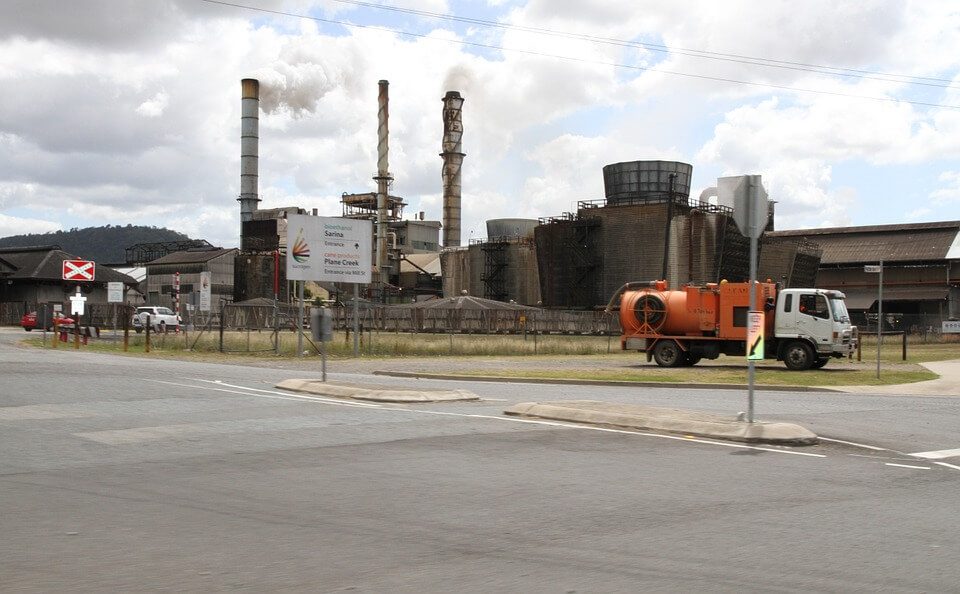

One of the alternative products that are used today to reduce reliance on fossil fuels is biofuel. Ethanol, for instance, is a type of biofuel derived from plant materials such as corn, sugar cane, or grasses. The consumption of ethanol fuel in the United States has increased exponentially over the past years, from 1.7 billion gallons in 2001 to 14.4 billion gallons in 2016, according to FuelEconomy.gov.
How ethanol is produced
Ethanol fuel in the country is produced through the dry mill or wet mill processing, which only differentiates in the initial treatment of the grains. Corn is the primary source of ethanol fuel in the U.S., although it can also be derived from cellulosic feedstock such as crop residues and wood.
Dry mills grind corns into flour before they are fermented into ethanol, while wet mills separate the corn’s starch, protein, and fiber before they are processed into ethanol and other products. About 90 percent of U.S. ethanol plants are dry mills because of their lower capital costs compared to wet mills. They are also concentrated in the Midwest due to their proximity to corn farms.
The benefits of using ethanol fuel
Ethanol is renewable and locally produced, which can help reduce dependence on oil exported from other countries. It is beneficial to the environment as it has lower carbon dioxide emissions. By 2022, the life-cycle greenhouse gas emissions from corn ethanol will be 43 percent lower than the baseline emissions from gasoline, according to a study by the U.S. Agriculture Department, per Herald-WHIG.
Ethanol fuel is blended to the gasoline in the U.S., usually at 10 percent called E10. There is also a blend containing 15 percent of ethanol called E15 and a blend called flex fuel or E85 with 51 percent to 83 percent of ethanol.
Ethanol production also provides jobs and income to rural America. In 2016, it accounted for almost 75,000 jobs in the region and contributed $42 billion in the gross domestic product.

Ethanol fuel can reduce the over-reliance to oil exports in the U.S. (Source)
Challenges facing the ethanol fuel industry
The ethanol fuel industry also faces challenges and opposition, mainly due to its impact on corn markets and land use. As farmers cleared more lands to plant corn, wildlife habitats are compromised.
Likewise, ethanol’s carbon footprint also increases. Farmers may also opt to plant corn and sacrifice other food crops for biofuel production, which would drive the prices of food. Moreover, there are arguments about its use in vehicles, as many old cars are not equipped to handle the amount of ethanol in gasoline.
Greenbelt Resources’ bioethanol solution
California-based Greenbelt Resources Corp. (OTCMKTS:GRCO) has developed an environmentally friendly process to produce bioethanol. Its proprietary waste-to-energy interconnected system called Paso Robles ECOsystem or PRECO uses a variety of feedstocks such as food waste, winery waste, and brewery waste to produce half a million gallons of bioethanol. Greenbelt’s bioethanol product appeals to companies looking for more sustainable, non-toxic and safer alternatives.
“PRECO is the solution to a challenge inherent in current local-scale technologies-their size. Unlike many traditional industrial-scale production technologies currently in operation, PRECO is designed and optimized for small- to medium-sized operations such as agricultural and beverage processors,” said Greenbelt Resources Chief Executive Officer Darren Eng in a statement.
“Our ecosystem concept enables the cost-effective transformation of wastes into value-added bioproducts including potable water. By creating value from waste, we help to boost the economy of the local community,” he added.
The global ethanol market is projected to reach $105 billion by 2022 at a rate of 7.9 percent CAGR.
—
This article may include forward-looking statements. These forward-looking statements generally are identified by the words “believe,” “project,” “estimate,” “become,” “plan,” “will,” and similar expressions. These forward-looking statements involve known and unknown risks as well as uncertainties, including those discussed in the following cautionary statements and elsewhere in this article and on this site. Although the Company may believe that its expectations are based on reasonable assumptions, the actual results that the Company may achieve may differ materially from any forward-looking statements, which reflect the opinions of the management of the Company only as of the date hereof. Additionally, please make sure to read these important disclosures.

-

 Impact Investing1 week ago
Impact Investing1 week agoFrance’s Nuclear Waste Dilemma Threatens Energy Future
-

 Fintech6 days ago
Fintech6 days agoKraken Launches Krak: A Game-Changing Peer-to-Peer Crypto Payment App
-

 Africa2 weeks ago
Africa2 weeks agoAgadir Welcomes Nearly 570,000 Tourists by May 2025
-

 Impact Investing15 hours ago
Impact Investing15 hours agoEuropeans Urge Strong Climate Action Amid Rising Awareness and Support
























You must be logged in to post a comment Login