Business
GDPR has already come into full force: Vital EU guidelines for entrepreneurs to remember
The GDPR has taken effect. Here’s a complete guide to ensure you are following the set guidelines if your business deals with European clients.

The rules set by the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) on April 27, 2018, are already distributed to 28 members of the European Union. Each country that cooperates with the EU should also take them into account. Let’s see how these rules are going to affect different kinds of business activities and pay attention to the strategy that partners of EU representatives may follow.
6 major principles of data handling according to GDPR
First of all, let’s be clear about what GDPR is. The doctrines below will give an idea of its concept:
- The EU residents gain a wider oversight over their personal info.
- All inhabitants of the EU work under standardized data protection policy.
- Those who fall under GDPR guidelines get the double-safe protection of individual details.
Another thing to clarify is personal data. The following show what it involves:
- Identifying information including address, phone number, first name, last name, passport ID, etc.
- Data that could be accessed through the internet: cookies, IP, etc.
- Medical records
- Biometric features
- Records as for the racial and ethnic backgrounds
- Religious opinions and personal views
© Nataliia Kharchenko
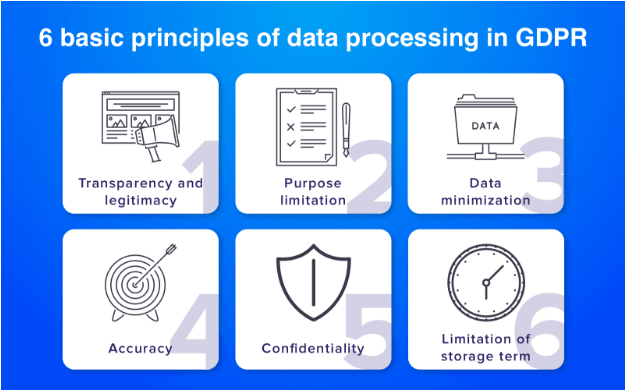
Finally, we’ve come close to the core points of data handling in GDPR. There are six of them:
Transparency and legitimacy. Identity details can be compiled and used with legal and fair background only. People should have a free access to the details about objectives and data-processing techniques.
Precise basis. The records can be gathered and utilized solely with the intention stated by the organization.
Minimum data collection. You are allowed to compile exactly as much data as you can process.
Accuracy. Incorrect data is to be removed or fixed at the request of the client.
Limitation of the period of storage. You can maintain data solely during the time needed for the purpose of processing.
Privacy. Working with personal data, all institutions and companies should provide the top-level protection against illegal interference and utilization of data for illicit purposes.
© Nataliia Kharchenko
What kinds of business fall under GDPR rules?
First of all, you should understand that GDPR is compulsory for all kinds of business that are involved in data gathering and processing throughout the EU. The regulations also apply to institutions located beyond the borders of Europe but cooperating with European partners.
However, some sectors of economic activity types should prepare for new disciplines in the first instance. Let’s consider them in more depth.
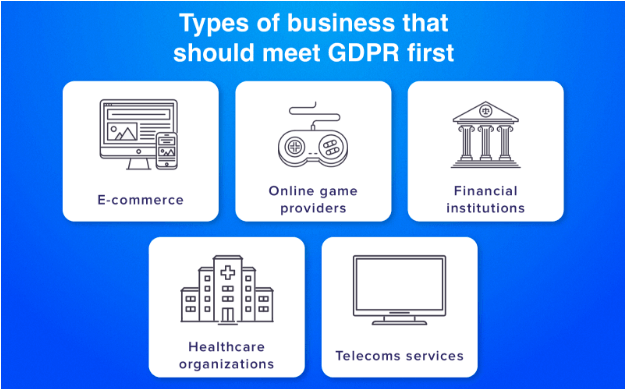
E-commerce. Online retailers receive and process individual details of thousands of users per day. To keep e-commerce business legal, entrepreneurs must necessarily follow GDPR rules.
Online gaming. Usually, users are required to establish their identity when playing an online game. Since May 25 (the date of entry into force of GDPR), online game providers should approach this issue more rigorously. Particularly, it extends to personal data related to children. At the moment, the age limit from which a teen can play online games varies from 13 to 16 years. The age limits are set in each country individually. The representatives of the gaming industry should make sure that the verification service is reliable enough to filter out too young users.
Financial organizations. Institutions that gain access to financial data, such as accounts numbers, credit cards numbers, bank records, etc. must follow GDPR rules perfectly.
Health institutions. Medical applications and sites that handle patients’ disease history, know about personal health issues and collaborate with hospitals and doctors should provide a highly effective online privacy based on the GDPR policy.
Telecommunication services. First of all, it refers to internet suppliers, which deal with a large number of people. They should offer guarantees that the personal records are processed only by informed consent of users.
© Nataliia Kharchenko
If your business falls under one of the above categories, you should revise your privacy policy urgently. Further, we are going to consider how to prepare for the newly introduced rules.
Basic points to prepare for GDPR
The main task of GDPR is to ensure the complete confidentiality of informational technologies and wide-scale network data transmission systems. Here is what you should do to get ready for it.
© Nataliia Kharchenko
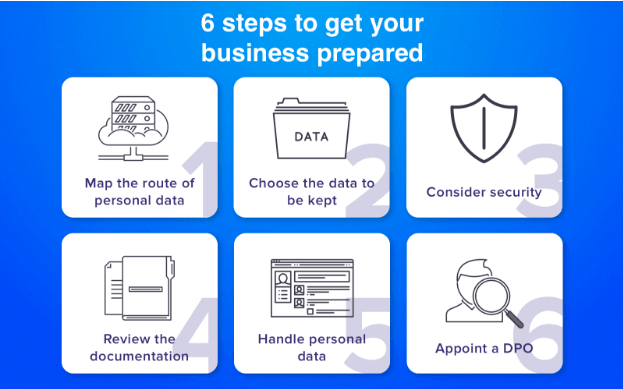
1. Define a full chain of entities that private data passes
At the initial stage, you need to develop a scheme that will assist you in visualizing the steps the information takes. In particular, you are going to learn:
- The source place
- The points of movement
- The final destination
Also, you need to clearly define the data size and amount and the actions which you perform on it. Do not forget to specify the persons who are hooked on the information and determine the risks associated with the processing.
2. Decide what details you will keep
According to GDPR terms, you can store the mandatory data only. Any expired, irrelevant or unnecessary information is to be immediately deleted. Pay proper attention to sorting the data and determine what value each piece of information generates.
3. Set up strong security
Security should be the first word that comes to your mind when palling around with personal information. Deploy the latest and cutting-edge technologies to protect private data of users. Develop an action plan which you will follow in case of information leakage. Remember to adhere to all the security-related issues when cooperating with contractors if you run a business in the form of outsourcing.
4. Work under a legal instrument
The terms of GDPR directive clearly specify that the processing of personal data is possible only if the user officially agrees to its use. Implicit consent is not a legal solution at all now. Given this, review all your papers, including agreements, affirmations and statements. Assure that they keep up to date with the standards of GDPR.
5. Determine the sequence of actions for processing private data
To do so, bear in mind that each person has eight rights according to GDPR policy. They are:
Partial entailment. Users may refuse to use their data for direct marketing purposes if they decide so.
Receiving notifications. You should keep the users advised about all the cases of data breach. They should receive an appropriate notification during the space of 72 hours since the moment when the data leak was detected for the first time.
Prohibition for data processing. A person may refuse to authorize private details processing but, at the same time, require the information not to be removed.
Private data modification. A person is at liberty to demand to change personal information if it is incorrect or outdated.
Removing content. If for some reason, customers stop cooperating with you, you should purge the logs immediately.
Passing the information. At will, customers may require to transfer their personal records to another service supplier.
Data access. Users are entitled to know of where, when and for what purposes their data is processed. You should provide this information immediately upon the request.
Being aware. You should inform the user that you are going to use his or her data. Any actions to interact with personal information are possible only after receiving a formal agreement.
6. Choose a reliable employee who will take responsibility for private information protection
Protection of personal data is relevant for the majority of business areas. To organize everything the best way, make sure that your Data Protection Officer has all the expertise necessary to do a good job.
Why GDPR is a right choice
If you want to work legally and provide a quality product to your customers, it is in your interest to follow the GDPR terms. Adherence or non-adherence to the policy has a direct impact on your income level. If you ignore or break the rules, you risk being fined up to 4 percent of the annual turnover or €20 million. From two sums, a bigger one will be selected.
Mean to imply that the doctrine is already in effect! Make sure that everything is prepared and set up to compile with the new standards.
How you benefit from GDPR innovation
Even though the newly introduced rules may seem too complex at first glance, they provide a lot of advantages:
- You can work according to a single standard and do not think about the specifics of information regulation in each EU country.
- A principal aim of the reform is to heighten an effect of economic performance and reduce bureaucracy in all the regions of the European Union. So, you can really benefit from following it.
- The new regulation is quite flexible and can vary depending on the type and volume of business.
- Keeping pace with the GDPR policy will certainly enhance the credibility of your clients.
Bottom line
Thus, on May 25, 2018, a valuable legislative document has entered into force. GDPR doctrine implements new standards for the collection, processing and storage of data in the countries of the EU. Any foreign partners cooperating with European clients should follow these norms to the full extent. The cooperation based on new standards is to improve the economic performance of all participants of the workflow and provide individuals with the reliable protection of the most sensitive information.
—
DISCLAIMER: This article expresses my own ideas and opinions. Any information I have shared are from sources that I believe to be reliable and accurate. I did not receive any financial compensation in writing this post, nor do I own any shares in any company I’ve mentioned. I encourage any reader to do their own diligent research first before making any investment decisions.

-

 Cannabis1 week ago
Cannabis1 week agoCanopy Growth Launches Cheaper 15g Medical Cannabis in Poland
-

 Fintech2 weeks ago
Fintech2 weeks agoFirst Regulated Blockchain Stock Trade Launches in the United States
-

 Crypto3 days ago
Crypto3 days agoUltimate Convenience: Why Consumers Expect Instant, Secure, and Borderless Payments
-

 Cannabis1 week ago
Cannabis1 week agoAurora’s Electric Honeydew Debuts in Poland, But Shared Registry Raises Patient Caution

























You must be logged in to post a comment Login