Business
JetBlue becomes the first U.S. air carrier to offer free WiFi connection
JetBlue Airways said it would begin to include the cost of wireless connections in its fares, effectively offering a fast WiFi connection to every passenger without extra cost.
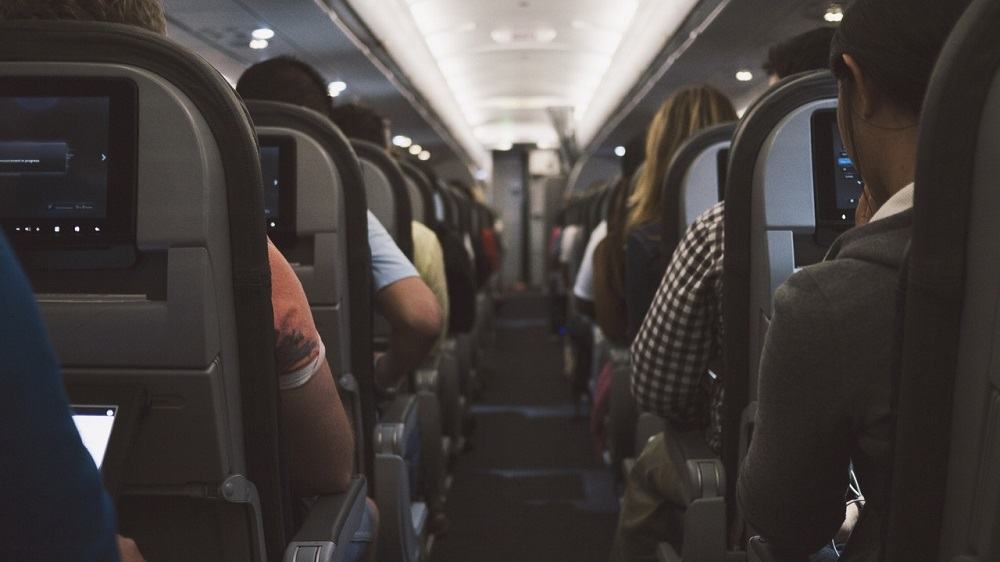

When it comes to travel, connectivity is essential these days. JetBlue became the first major U.S. air carrier to offer every passenger a WiFi connection while traveling by air.
Don’t take my word for it. Just ask Wendy Lewis, who says she spends a good part of every trip trying — and sometimes failing — to find reliable and reasonably priced hotspots. Airport lounges make connecting a cinch, she says. But the moment she boards a bus, plane or train, it’s a headache, with slow speeds, high bills, and frequent outages.
“It’s always a challenge for me and a point of tremendous frustration,” says Lewis, a beauty consultant from New York.
That’s a common sentiment. The release of a study on airport WiFi earlier this year and a move by JetBlue to include wireless service in its fares has sparked a broader conversation among travelers about connectivity and what they should expect in the future. Short answer: faster connections, same frustrations. But don’t worry, there are workarounds.
The research, published by Speedtest by Ookla, an Internet testing, and metrics company, examined the 20 American airports with the most passenger boardings. It reviewed the results of consumer-initiated Speedtest data for the four largest cellular carriers as well as airport-sponsored WiFi at each location and found that Denver, Philadelphia, and Seattle offered the fastest wireless connection speeds. The slowest: Atlanta, Orlando, and San Francisco.
Earlier this year, JetBlue Airways said it would begin to include the cost of wireless connections in its fares, effectively offering a fast WiFi connection to every passenger without extra cost. In doing so, JetBlue became the first major U.S. air carrier to give every passenger a wireless connection and possibly has paved the way for wireless Internet connections to be included in the cost of other airline tickets.
In a related development, American Airlines announced in January that its new Boeing 737 Max aircraft, scheduled to be delivered later this year, would not have seat-back entertainment systems, noting that most of their passengers bring their own devices. That’s bound to boost appetites for onboard WiFi.
“Connectivity is as essential as the air we breathe,” says Dawn Callahan, the chief marketing officer at Boingo Wireless, which offers cellular and WiFi connectivity to travelers. She says demand for its product has increased twentyfold in just five years, thanks to travelers’ voracious appetite for fast wireless connections. The majority of business travelers carry three devices — usually a phone, a tablet and a laptop computer. Adds Callahan, “We’ve never seen more WiFi usage than we do today.”
The numbers back up that assertion. A Research+Data Insights study commissioned by Red Roof Inn found that 7 in 10 travelers say that fast, accessible WiFi is more important than a hotel’s location, parking facilities and even free breakfast. Where do travelers want to connect? Almost everywhere. A survey by Xirrus, a provider of high-density WiFi, found that 83 percent of users connect at hotels, 72 percent log on at cafes and 64 percent use airport hotspots.
“WiFi is no longer a luxury,” says Gary Griffiths, chief executive of wireless connectivity company iPass, “but an expectation.”
And that’s the problem. Everyone wants to be online, and wireless providers are having trouble keeping up with demand. A Cisco study predicts that by 2020, the number of wireless hotspots worldwide will rise to 432 million, a sixfold increase.
Consider the experience of frequent business travelers such as Andy Abramson, a Los Angeles communications consultant who practically lives on the road. Airports know that they must offer WiFi, “but with more people carrying more devices, the networks often are overloaded and not really useful for much more than Web browsing and email,” he says. “Streaming eats up a lot of bandwidth, and most airport networks just can’t handle that many people listening or watching streamed content.”
Abramson prefers heading to one of the airport lounges, which offer their own networks to members — at a price. Failing that, he logs on with his Boingo subscription account, which offers a speedier connection than Boingo’s free WiFi offering. (Boingo charges $9.95 a month for Abramson’s unlimited premium plan.)
Alex Gizis, the co-founder of Speedify, a company that develops apps that optimize your Internet for speed and security, says that we have reached a tipping point in travel. Both demand and frustration are so high that people are giving up in their attempts to connect.
“More people are hitting hotspots that don’t work,” he says. “That’s so frustrating that people actually just give up on WiFi.”
The travel industry is trying to keep up with demand. For example, hotels are moving toward speedier 5 GHz hotspots, an upgrade from the industry standard, a 2.4 GHz wireless access point. But, says Matthew FitzGerald, a systems engineering manager for Ruckus Wireless, a manufacturer of wireless networking equipment, the upgrade has been a challenge. “Not everyone has made these changes, and some have done them incorrectly,” he says.
At the rate they’re going, it’s unlikely that they ever will meet the demand by customers in an always-on society.
“I live and die by WiFi,” explains Alexandra Mandel of Ambler, Pa., a business-development manager for a company that organizes executive retreats. In fact, she can’t plan a conference without guaranteeing that the participants will have access to reliable wireless connections.
And yet, she regularly finds herself on planes without a connection or at hotels where the only wireless access point can be found in the lobby — or for a steep price. The wireless-free planes are the greatest mystery to her.
“It’s 2017,” Mandel says. “Why don’t we have WiFi on all planes?”
The short-term fixes are inelegant, at best. Travelers can subscribe to a service such as Boingo or carry their own wireless hotspot from a cellular provider. (The Ookla survey also rates those; Detroit, San Francisco, and Minneapolis are the fastest.) Or they can take their chances with the strained networks at their airport or hotel, or aboard their aircraft.
Down the road, it’s up to the industry to develop better standards that offer faster connection speeds, perhaps with the encouragement of bandwidth-starved travelers and legislators who are embarrassed by the fact that many other countries offer better connection options than the United States.
Kevin Robinson, the vice president of marketing for industry trade group Wi-Fi Alliance, says that in the short term, new technology may ease some of the pain.
“In 2017, travelers will benefit from more seamless and secure access to WiFi networks, resulting in a better overall experience with WiFi while traveling,” he says. Many hotels and airports are deploying a new standard called Wi-Fi Certified Passpoint networks, which allows users to skip the lengthy authenticating process for each new WiFi network. Instead, you just log in once.
If only getting connected were always that easy.
—
DISCLAIMER: This article expresses my own ideas and opinions. Any information I have shared are from sources that I believe to be reliable and accurate. I did not receive any financial compensation in writing this post, nor do I own any shares in any company I’ve mentioned. I encourage any reader to do their own diligent research first before making any investment decisions.

-
 Business2 weeks ago
Business2 weeks agoDow Jones Near Record Highs Amid Bullish Momentum and Bearish Long-Term Fears
-

 Africa2 days ago
Africa2 days agoCameroon’s Government Payment Delays Exceed 200 Days, Straining Businesses and Public Finances
-

 Crowdfunding1 week ago
Crowdfunding1 week agoThe Youth Program at Enzian Shooting Club Is Expanding Thanks to Crowdfunding
-

 Crypto5 days ago
Crypto5 days agoTariff Turmoil Sends Bitcoin and Ethereum Lower as Crypto Markets Face Mounting Pressure























You must be logged in to post a comment Login