Business
Batteries have come a long way: Here’s what the future holds
We use batteries in our daily lives from our laptops to smartphones. Here are the changes in the battery industry and its technological advancements.

The surge in demand for sustainability and accountability has advanced the research and development of batteries in recent years. Here are some changes made and what people can expect in the future.
Main changes in battery industry
The lithium-ion battery has been the rage because of the rise in demand of electric vehicles. However, li-ion batteries can still be improved a lot in terms of reliability. Sourcing these power packs also have drawbacks: they are mined in developing countries, they are volatile, and they contain limited power in them.
Tesla has made significant changes to address some of these concerns. According to Renewable Energy, the company reduced the amount of cobalt in their batteries. Cobalt is sourced from conflict countries such as Democratic Republic of Congo. Some issues that are connected to its mining are child labor and unsafe work practices.
Companies are raising accountability by demanding where Cobalt is sourced from. However, tracking if the mineral is ethically sourced remains challenging because processing plants such as in China tend to mix materials from different mines indiscriminately.
Tesla Model 3 batteries allegedly contain only 3 percent cobalt, and it wants to further lessen it in the future. Other chemical companies such as LG Chem Ltd. and SK Innovation Co Ltd. from Korea promise to do the same.
Aside from making sure that minerals used in batteries are from non-conflict areas, manufacturers are promising safer batteries. Samsung and Boeing Dreamliner have been in hot seats in the past due to exploding power packs. To avoid such incidents, battery manufacturers are looking to replace liquid electrolyte with solid state batteries.
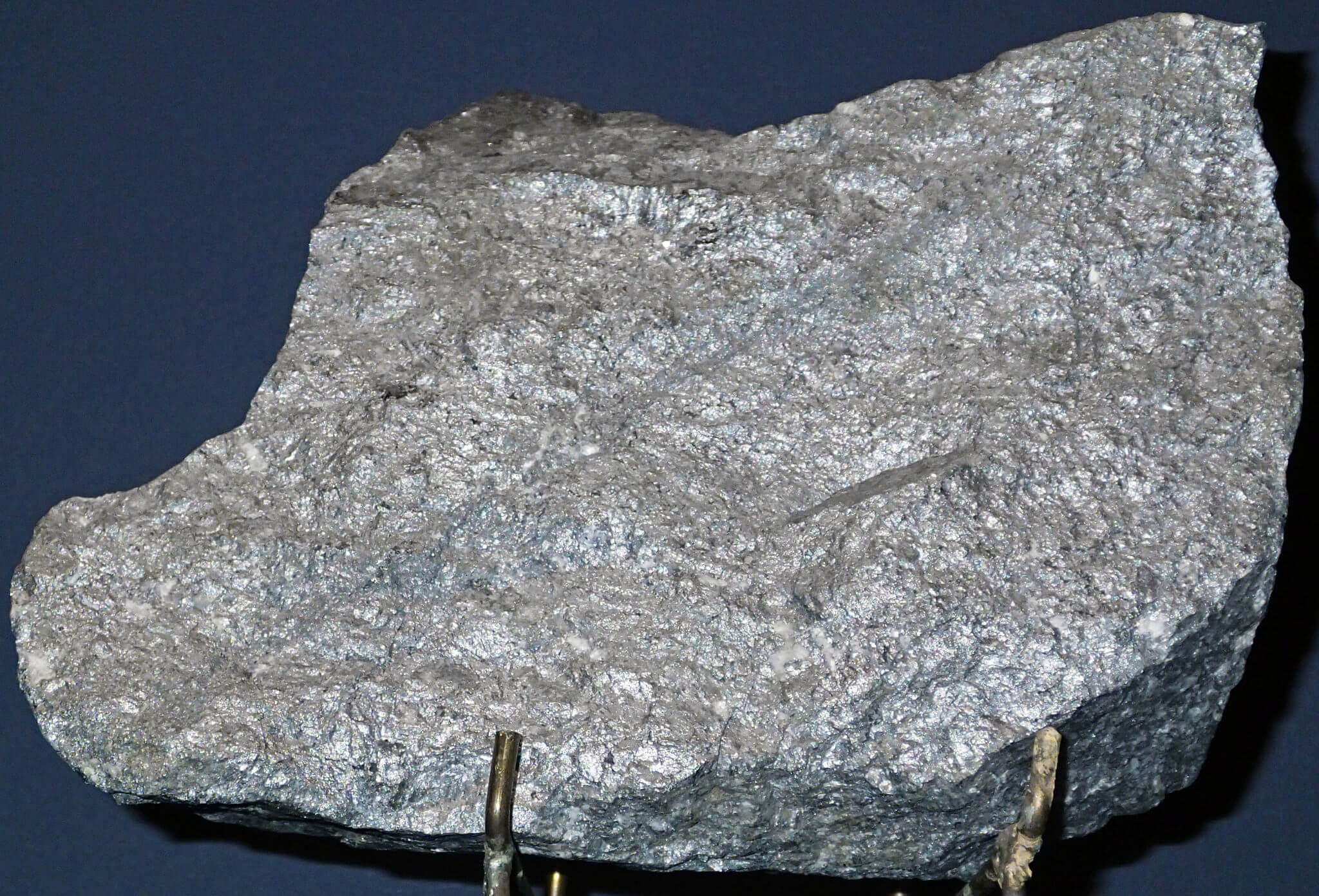

Companies are raising their concern for cobalt, the main ingredient of batteries, whether it is ethically sourced and do not come from conflict areas such as the Democratic Republic of Congo. (Photo by James St. John via Flickr. CC BY 2.0.)
A French company called Blue Solutions is already commercially producing solid state batteries, and they have collaborations with car companies such as Daimler and Citroen. Blue Solutions is set to debut its solid state battery next year with improved stored energy.
Batteries that don’t ever die? It could be a possibility sooner than later using triboelectric nanogenerator. The power harvesting technology can source energy from the device wearer.
Other companies gaining from the trend
The progress Tesla and Blue Solutions have made inspired other companies such as Dyson to think outside the box and take advantage of the momentum electric vehicle companies have.
Dyson is planning to make electric vehicles from their Singapore plant. The company is known to produce premium home appliances and the leap to make EVs is worth commending. Dyson is targeting to launch its first EV in 2021.
Graphenano is spearheading research that could lead to supercharged graphene batteries supplying an EV with range of up to 500 miles on a single charge.
As technology progresses, the feasibility of other ideas are being studied on if they can make it to commercial use. There are transparent solar chargers, air charging, foldable batteries, laser-made microsupercapacitors and foam batteries. The development of wealth of options for battery use not just for electric vehicles but for everyday appliances as well is hoped to bring down costs of materials for such products.

-

 Impact Investing1 week ago
Impact Investing1 week agoCDP Approves €1.5 Billion Package to Boost Industry, Renewables, and International Development
-

 Crypto2 weeks ago
Crypto2 weeks agoUniswap and BlackRock Partner to Launch BUIDL in DeFi
-

 Impact Investing2 days ago
Impact Investing2 days agoThe Sustainability Revolution: Driving a Net-Zero, Nature-Positive Economy
-

 Biotech1 week ago
Biotech1 week agoNew Molecular Clues Explain Aggressive Neuroblastoma and Point to Targeted Treatments























You must be logged in to post a comment Login