Business
The status of alternative energy jobs in the US
The U.S. is cutting down its reliance on coal energy.
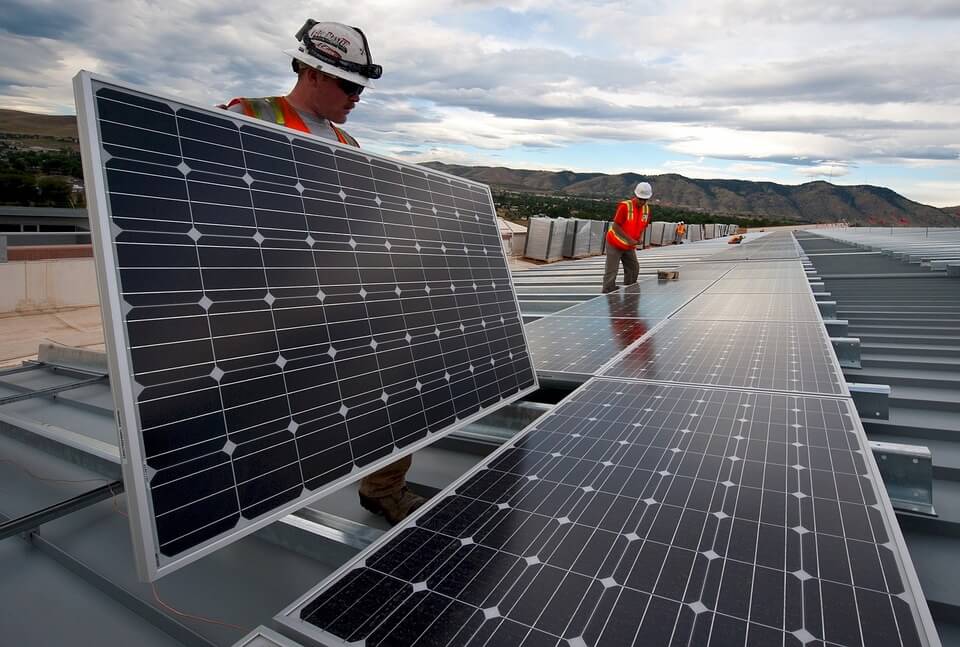

Energy is one of the most important facets of our daily life. Without precious energy, we’re unable to do our work to be able to progress or enjoy the little creature comforts we have at home.
The state of energy sources like coal
In the United States, one of the major sources of energy is coal. The U.S. Energy Information Administration said that in 2016, coal accounted for 30% of the electricity generated in the country which is used by power plants to make steam. On the other hand, other industries that use steam from coal include paper industries.
While coal has proven to be useful in the energy sector, there are some downsides to it as well. Just some of the ill effects of coal mining include changing the landscape through the mountaintop removal and valley fill mining method which can pollute and harm aquatic wildlife downstream and underground mining which can cause the land to collapse from above and acidic water that could drain from abandoned mines. Another ill effect of coal mining is the emissions from burning coal. In 2014, methane emissions from coal mining and abandoned coal mines accounted for 10% of the total U.S. methane emissions and 1% of U.S. greenhouse gas emissions.
With that in mind, governments such as the U.S. are seeking ways to address the issue on the negative effects of coal by implementing the Clean Air Act and looking at greener and safer alternative energy sources.
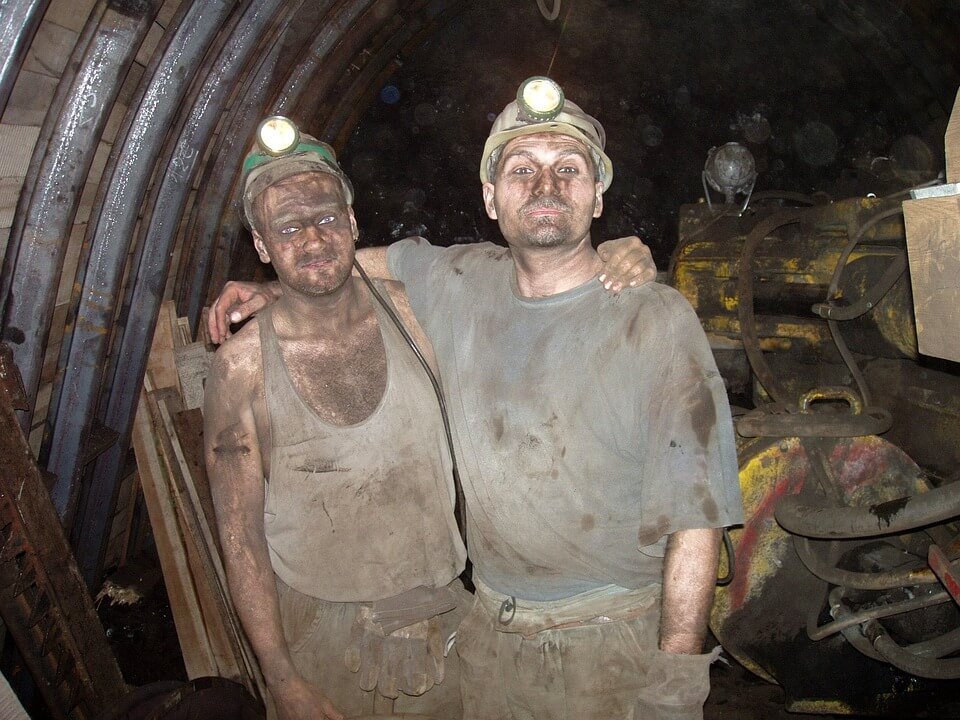

The U.S. is trying to balance the need for coal as a power source and limit its damages in the environment. (Source)
Energy sector manpower
It takes the knowledge and the skills of trained individuals in helping to maintain the current energy sector. While safer energy sources are now favored compared to that of coal, it also reflects on the manpower needed in the industry. According to an article by The New York Times, the popularity of jobs in the coal industry fell since 2012. The industry only employed 160,000 workers in the U.S., while there were 54,000 coal jobs in mining in 2016.
Meanwhile, in the same year, 1.9 million Americans held jobs in electric power generation, mining and other fuel extraction activities. In terms of solar energy, 373,000 Americans worked part time or full time in the solar energy, and 260,000 worked on solar projects. Moreover, the Midwest and the Great Plains had more rates of wind energy employment, and a testament to this is that the region has been a leader in renewable power generation.
The future of alternative energy jobs
The perfect example of how energy jobs are slowly shifting to alternative energy is in Wyoming and West Virginia. Both states are heavily reliant on fuel extraction. However, with the fall of energy prices and the use of coal, workers by the thousands have lost their jobs. Wyoming is known for its production of coal, but a Chinese firm that makes wind turbines are setting up a training program for technicians for a large power plant. Meanwhile, in West Virginia, Solar Holler, a non-profit, struck a deal with Coalfield Development to provide training for solar panel installers.

-

 Crowdfunding2 weeks ago
Crowdfunding2 weeks agoSavwa Wins Global Design Awards and Launches Water-Saving Carafe on Kickstarter
-

 Business6 days ago
Business6 days agoDow Jones Nears New High as Historic Signals Flash Caution
-

 Crypto3 days ago
Crypto3 days agoBitcoin Surges Toward $110K Amid Trade News and Solana ETF Boost
-

 Fintech1 week ago
Fintech1 week agoMuzinich and Nao Partner to Open Private Credit Fund to Retail Investors























You must be logged in to post a comment Login