Business
Zinc is one of the most important metals—here’s why
People don’t realize the importance of zinc, but it has various applications in their daily lives.
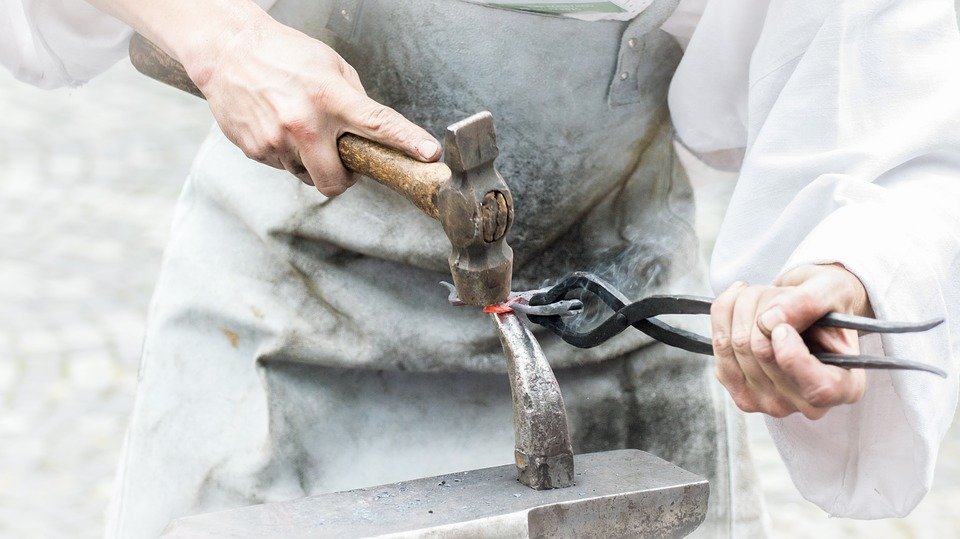

Zinc is one of the most versatile and in-demand metals in the world: in industry, manufacturing, medicine, agriculture and for human health. It doesn’t have the same allure and mystique as precious metals like gold or silver, but modern civilization will not be the same without it.
Lately, because of a global shortage in zinc, the base metal has been in the news rather often—that is, in news related to commodities trading. This is a good time as any to look at some facts about zinc and its role in our daily lives.
Zinc was “discovered” several times
Ancient artifacts, specifically brass implements, discovered in Palestine were found to contain zinc. The items, dated between 1400-1000 BC used a combination of zinc and copper. The Greeks and Romans apparently used it as well. This was way before this base metal had been identified as a distinct element.
Then in 1746, German chemist Andreas Marggraf discovered, or rediscovered zinc, identifying it as a separate element. Marggraf wrote extensively about his discovery leading many to credit him with the find. However, two others had made the same discovery several years earlier: William Champion in England in about 1740 and Anton von Swab in Sweden in 1742.
Outer space
Zinc is not only mined here on Earth but can be the by-product of cosmic events: when a star turns supernova and explodes, essentially, dying, it releases minerals, including zinc.
Body essential
Human beings need zinc, as a trace element, to stay healthy and survive. Normally, an individual would have 2-3 mg of zinc in his or her body, which is used up and replenished through food sources and supplements.
All of the cells in the human body contain zinc, and the element plays a role in many physiological processes. It keeps the immune system functioning normally, and is important in letting cells grow, divide, and re-grow to repair injuries. It also helps humans’ senses of smell and taste.
A human baby in the womb needs this element in order to develop and grow. A deficiency in zinc leads to health problems like frequent infections, poor wound healing, vision problems, hair loss, and others. It could also lead to hormone problems in the reproductive organs: testes and ovaries.
The human eye, and in males the prostate, have the highest concentrations of this metal in the body. Interestingly, semen contains about 135 micrograms of zinc.
Oysters contain high levels of the said metal. Since zinc is important for hormone regulation, including reproductive hormones, this may be the basis for thinking oysters are aphrodisiacs.
Still more on human reproduction: scientists discovered that when an egg absorbs a sperm cell, it releases “sparks” zinc, leading them to speculate on whether other roles the said element may play in the process.
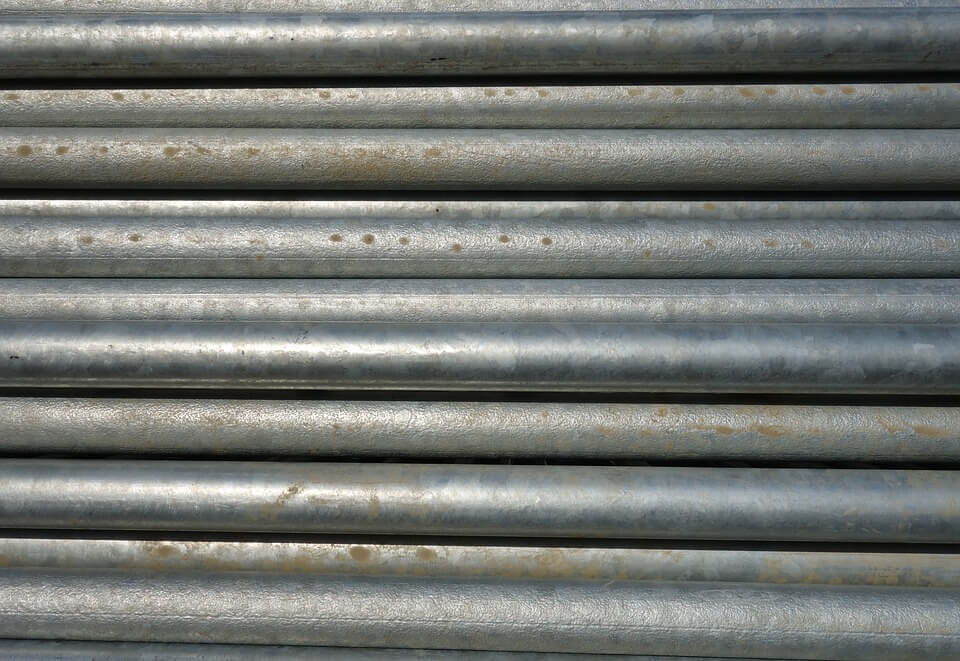

The importance of zinc cannot be underestimated. It strengthens most metals used in construction and manufacturing. (Source)
Workhorse metal
Zinc is invaluable in construction and manufacturing activities. Steel and iron need to be galvanized, or coated, in this base metal to protect them from rust and corrosion. Everything, from buildings, to bridges, roads, railways, cars, trucks, and even aircraft, needs zinc coatings for various components.
It is also used in battery manufacturing and in agriculture as a component of organic fertilizer. In the health industry, it is an ingredient in many food supplements.
These diverse uses make it the fourth most in-demand metal in the world. This is why, in the face of the global shortage of zinc, miners and explorers are looking into new zinc deposits under the earth.
China’s growing demand
China is now in the middle of a massive urbanization and industrialization program. It is currently building megacities meant to house some 50 to 100 million people (or more). This is why it is the country with the highest demand for zinc today. Not only does it need the base metal for infrastructures like skyscrapers and bridges, but also for a new railway network to interconnect its cities.
Humans will continue to need zinc as long as they need the conveniences of modern life. It also plays a role in human physiology. As such, the base metal will remain invaluable for a long time to come.

-

 Business1 week ago
Business1 week agoDow Jones Nears New High as Historic Signals Flash Caution
-

 Crypto1 week ago
Crypto1 week agoBitcoin Surges Toward $110K Amid Trade News and Solana ETF Boost
-

 Fintech2 days ago
Fintech2 days agoRipple and Mercado Bitcoin Expand RWA Tokenization on XRPL
-

 Crypto1 week ago
Crypto1 week agoBitcoin Traders on DEXs Brace for Downturn Despite Price Rally
























You must be logged in to post a comment Login